
 |
 |
|
|
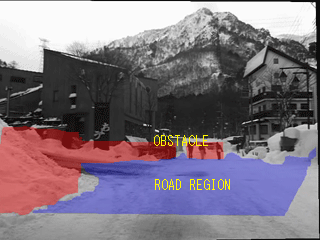
Obstacle detection results |
||

|

|
||
|
Fig. Straight line structre objects detection&discrimination results (Green line:Road lane marker, Red region: Obstacle region) |
|||
 |
|
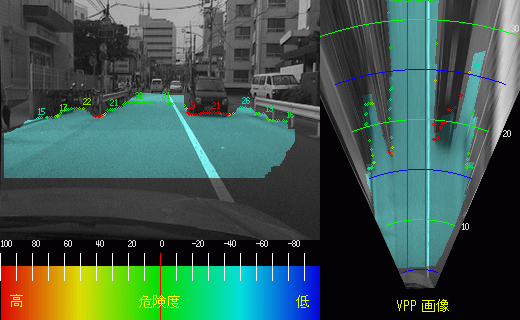
Dangerous region detection result |
 |
|
Ego-motion estimation result |
|
|
|
|
| Road region extraction results | ||
| abstract In this paper, we propose a method for ego-motion estimation using vehicle-mounted stereo cameras. Estimating ego-motion using cameras requires extraction of static regions from the images. We first extract static regions which correspond to the road plane and estimate the pose of the road plane using stereo images. Then, we back-project the extracted region onto the road plane. The vehicle ego-motion can be obtained by matching extracted road regions between sequential images. Our matching method consists of two steps. The first step utilizes a vehicle motion model to estimate three motion parameters, two for translation and one for rotation, simply and robustly. In the second step, the estimated parameters in the first step are iteratively updated by using a gradient method to obtain more precise estimation. Finally, we present experimental results to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method. |
| abstract In this paper, we propose the method for an obstacle detection on the road plane using the stereo cameras mounted on a vehicle. We first estimate planar regions using projective transformation matrix. By singular value decomposition of the matrix, we get the normal vector of the planar regions and the distance from the optical center of the primary camera to the plane. Then, we make a virtual projection plane (VPP) image which is equivalent to the top view of the road scene. Obstacles are detected by checking the change of the planar regions using the VPP image. Finally, we present the experimental results of obstacle detection with our method. |
| abstract In this paper, we propose a robust method to estimate planar regions using sequential stereo images for visual navigation of an autonomous vehicle. The proposed method estimates 2-D projective transformations dynamically, which represent planes in space, for both stereo images and sequential images. This can be done robustly by utilizing sequential information, i.e. previous estimation of both the projective transformations and the planar region. In addition, a method for preventing misdetection due to textureless areas is proposed. The experimental results, using sequential stereo images taken from a moving vehicle, have shown that the proposed method can work robustly even in the conditions of undulation of the road and rolling and pitching of the vehicle. |
| abstract In this paper, we propose a robust method to estimate planar regions using sequential stereo images for visual navigation of an autonomous vehicle. The proposed method estimates projective transformations, which represent the plane in space, for both stereo images and sequential images. This can be done robustly by utilizing sequential information, i.e. previous estimation of both the transformations and the planar region. Also, the method to prevent misdetection due to "textureless" is presented. The experimental results, using sequential stereo images taken from a moving vehicle, show that the proposed method can work robustly even in the condition of undulation of the road and rolling and pitching of the vehicle. |
| Back to Page Top |
Last Update 2006.9.5 |