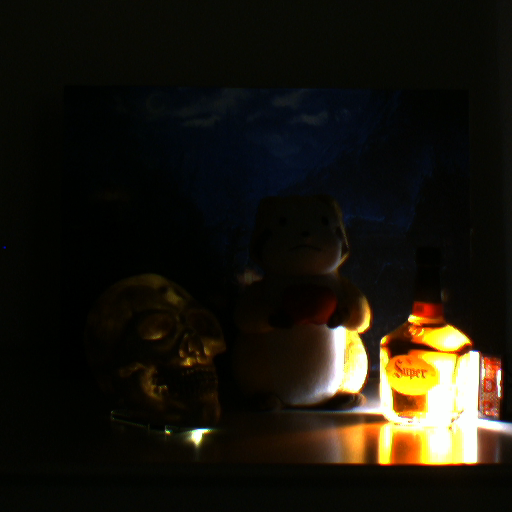
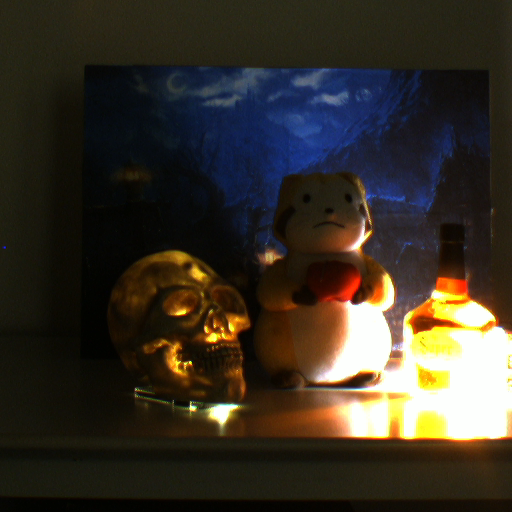
Super High Dynamic Range Imaging
We propose a novel high dynamic range (HDR)
imaging algorithm for the scenes that contain an extremely wide
range of scene radiance. In the HDR imaging, several images
are taken under different exposures. Those images usually have
displacement from one another due to camera and/or object
motions. The challenge of the super HDR imaging is to align
those images because any image contains “lost” regions where
texture information is completely lost due to overexposure or
underexposure. We propose an image alignment algorithm based
on similarities of region shapes instead of the similarities of
the textures.
Datasets and source code can be found
here.
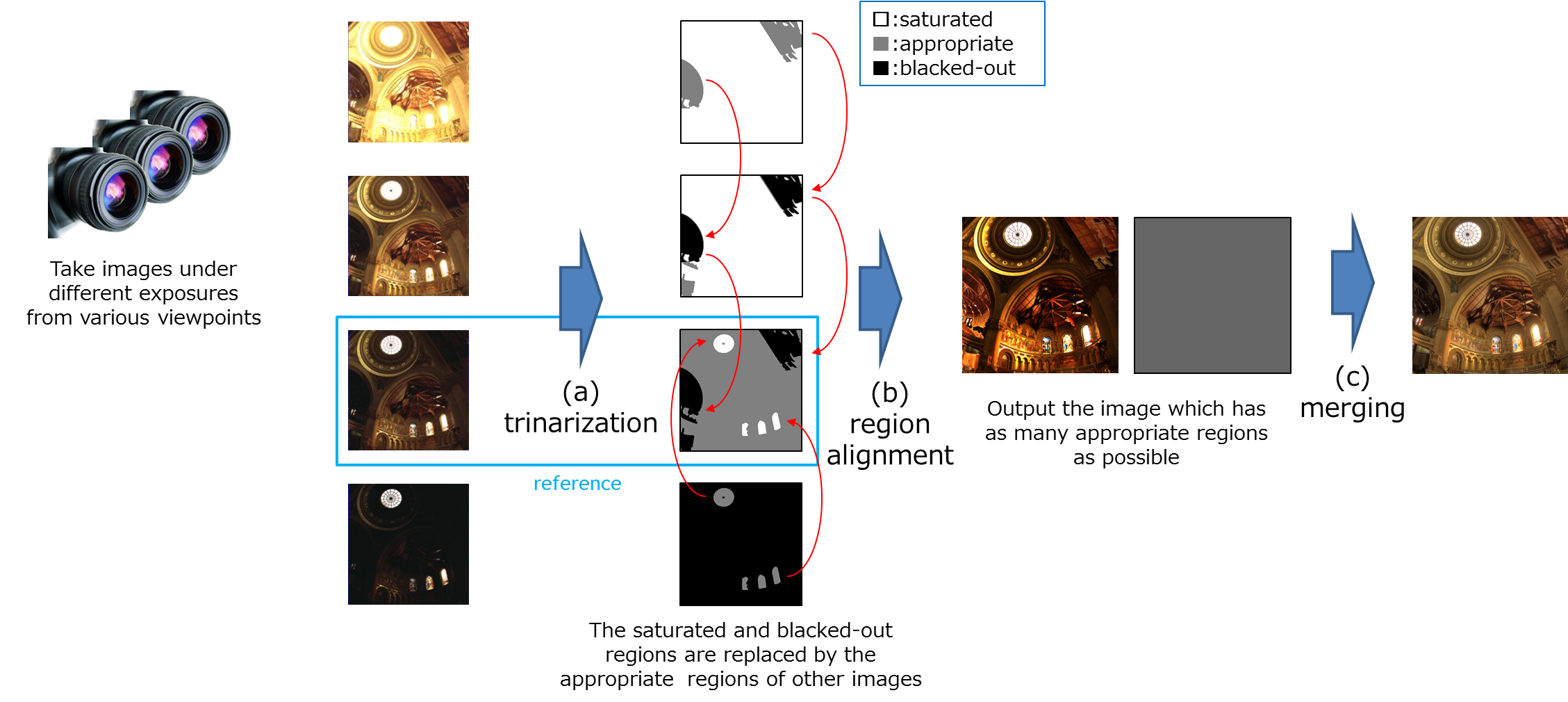 |
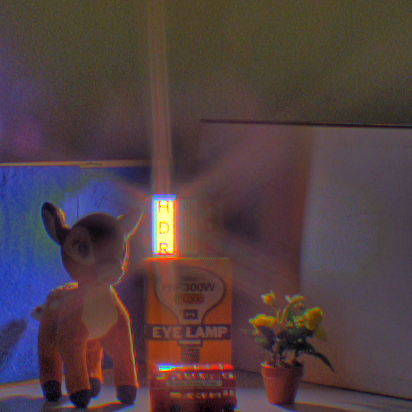
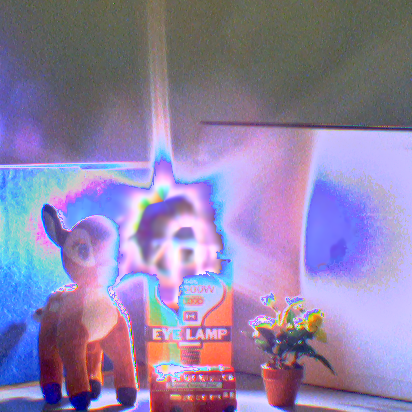
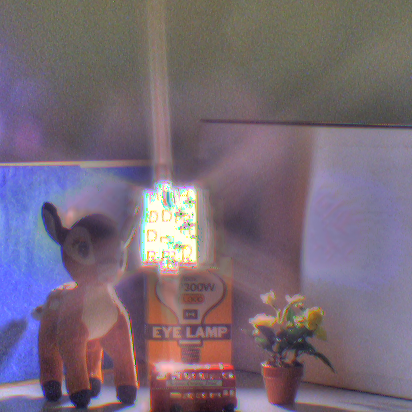
| Fig. Here, (a), (b), and (c) are overviews of our algorithm. (a) All input images are trinarized by luminance into three regions: saturated, appropriate, and
blacked-out. Then, the image with the largest area of the appropriate region is defined as the reference image. (b) Images are aligned based on the shapes of
segmented regions. (c) The HDR image is composed by merging aligned images. |
Compared Algorithms
[1] Y. S. Heo, K. M. Lee, S. U. Lee, Y. Moon, and J. Cha, “Ghost-free high dynamic range imaging,” in Computer Vision–ACCV 2010. Springer, 2011, pp. 486–500.
[2] P. Sen, N. K. Kalantari, M. Yaesoubi, S. Darabi, D. B. Goldman, and E. Shechtman, “Robust Patch-Based HDR Reconstruction of Dynamic Scenes,” ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) (Proceedings of SIGGRAPH Asia 2012), vol. 31, no. 6, pp. 203:1–203:11, 2012.
Publication
Super High Dynamic Range Imaging
Takehito Hayami, Masayuki Tanaka, Masatoshi Okutomi, Takashi Shibata and Shuji Senda
Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 2014 [
PDF] [
dataset] [
code]
セグメンテーションに基づくスーパーハイダイナミックレンジ画像合成
速水健人, 田中正行, 奥富正敏, 柴田剛志, 仙田修司
第20回画像センシングシンポジウム(SSII2014), pp.IS1-39-1-6, June, 2014

















