Joint Design of Camera Spectral Sensitivity and Color Correction Matrix with Noise Consideration
Xinyue Yu, Masayuki Tanaka, Yusuke Monno, and Masatoshi Okutomi
Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo, Japan
Electronic Imaging (EI2024)
Abstract
Camera spectral sensitivity (CSS) establishes the connection between scene radiance and device-captured RGB tristimulus values. Since the spectral sensitivity of most color imaging devices typically deviates from that of human vision or a standard color space and also noise is often introduced during the process of photoelectric signal conversion and transmission, the design of an efficient CSS with noise robustness and high color fidelity is of paramount importance. In this paper, we propose a CSS optimization method with noise consideration that designs theoretically an optimal CSS for each noise level. Additionally, taking practical considerations into account, we further extend the proposed method for a universally optimal CSS adaptable to diverse noise levels. Experimental results show that our optimized CSS is more robust to noise and has better imaging performance than existing optimization methods based on a fixed CSS.
Methodology Overview
In this paper, we have proposed a method to derive a theoretically optimal CSS. We have first introduced an individual optimization method for jointly designing CSS and CCM in single-noise-level cases. Additionally, taking practical considerations into account, we further have extended the method to derive a commonly optimal CSS for the multi-noise-level case, as illustrated in Fig.1.
Simultaneously, considering the color reproduction performance of the optimized CSS, we have incorporated a weighting parameter μ into the optimization function, simulating the denoising algorithm's role in the assumed imaging pipeline.
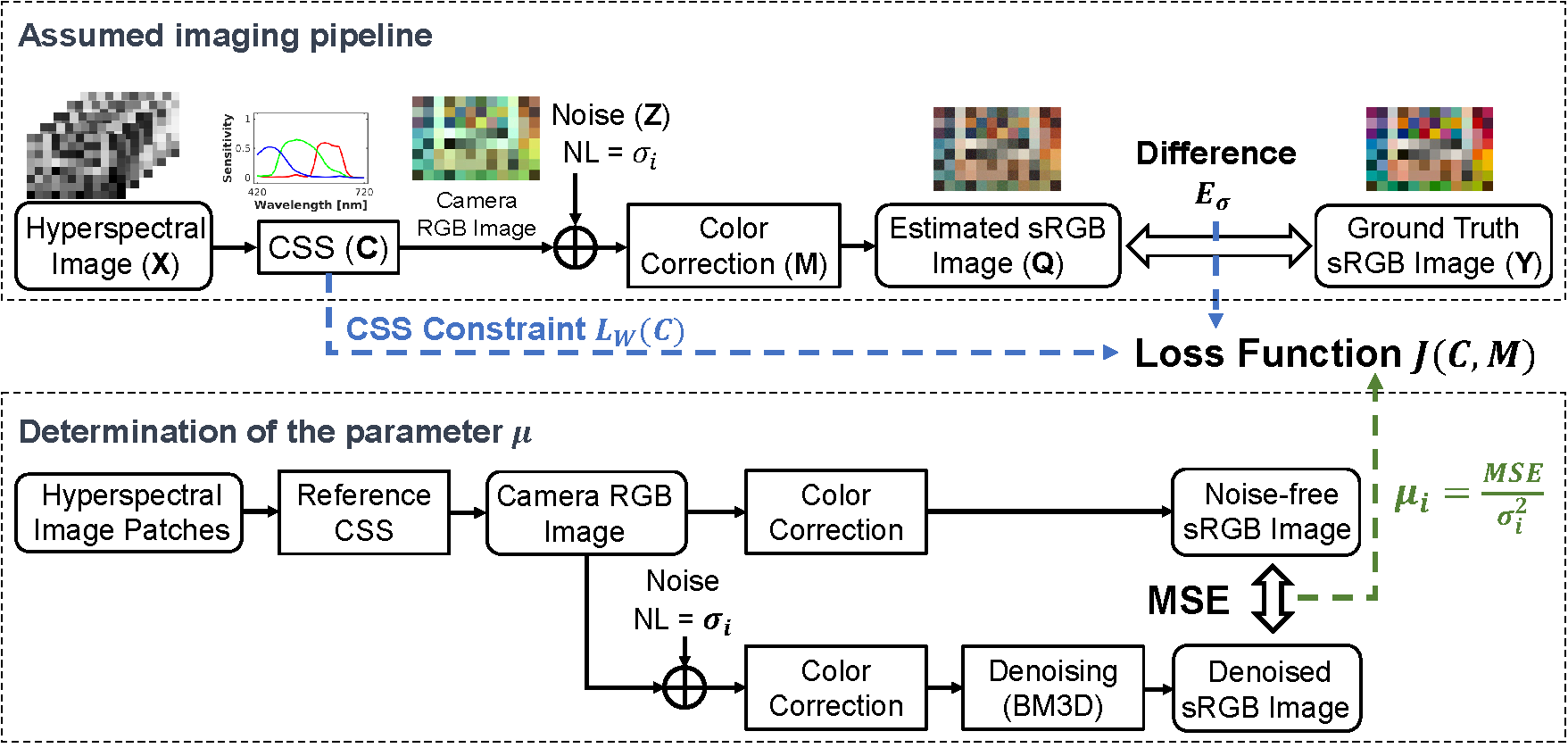
Loss Functions
Loss Function for Individual Optimization:
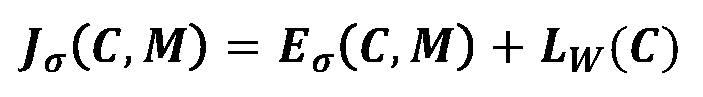
Let σ be a given noise level. Theoretically, we can individually optimize the paired CSS C and the CCM M for each given noise level, denoted as individual optimization.
Loss Function for Common Optimization:
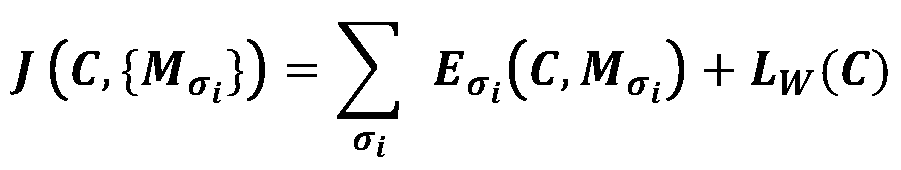
However, it is infeasible to change the CSS for each noise level in practice. Thus, we propose to optimize one CSS matrix and multiple CCM corresponding to the set of assumed noise levels.
Experimental Results and Visualization Examples
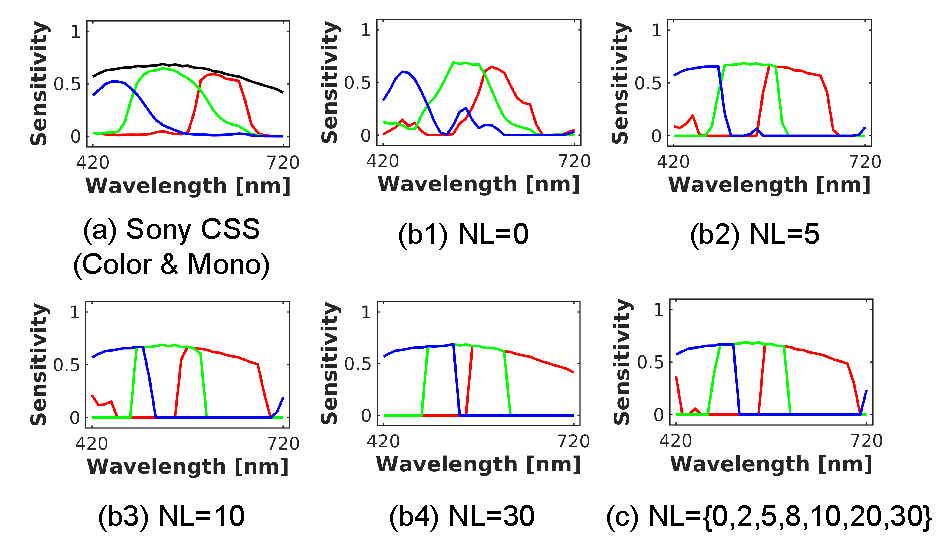

Download Materials
Publication
- Joint Design of Camera Spectral Sensitivity and Color Correction Matrix with Noise Consideration [Link]
- Xinyue Yu, Masayuki Tanaka, Yusuke Monno, and Masatoshi Okutomi
- Electronic Imaging (EI), January, 2024.