2019.5.1. Update. Add the link to an evaluation tool for visual localization on InLoc dataset.

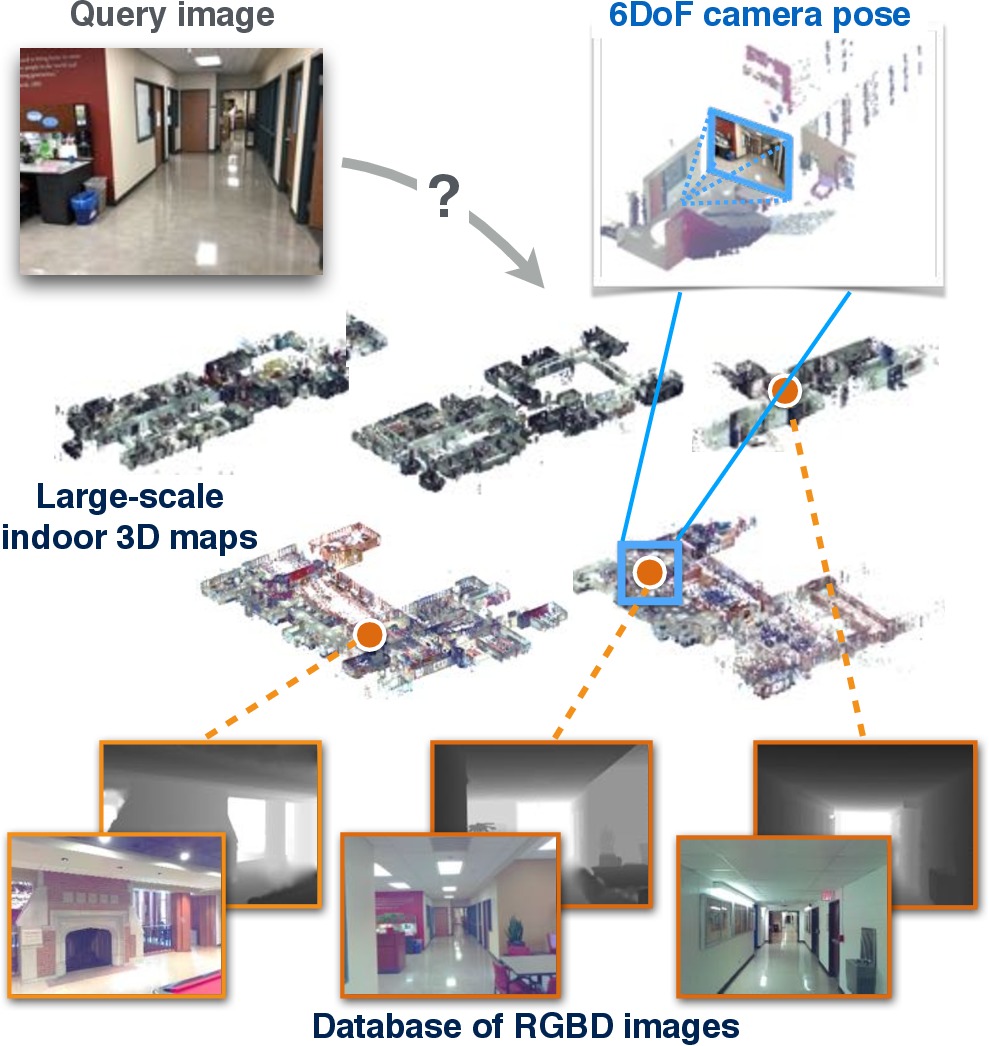
We seek to predict the 6 degree-of-freedom (6DoF) pose of a query photograph with respect to a large indoor 3D map. The contributions of this work are threefold. First, we develop a new large-scale visual localization method targeted for indoor environments. The method proceeds along three steps: (i) efficient retrieval of candidate poses that ensures scalability to large-scale environments; (ii) pose estimation using dense matching of higher-level structures rather than local features to deal with weakly textured indoor scenes, and (iii) pose verification by virtual view synthesis to cope with significant changes in viewpoint, scene layout, and occluders. Second, we collect a new dataset with reference 6DoF poses for large-scale indoor localization. Query photographs are captured by mobile phones at a different time than the reference 3D map, thus presenting a realistic indoor localization scenario. Third, we demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms current state-of-the-art indoor localization approaches on this new challenging data.
Hajime Taira, Masatoshi Okutomi, Torsten Sattler, Mircea Cimpoi, Marc Pollefeys, Josef Sivic, Tomas Pajdla, Akihiko Torii. InLoc: Indoor Visual Localization with Dense Matching and View Synthesis. In: CVPR 2018. [bibtex] [ArXiv preprint]
Hajime Taira, Masatoshi Okutomi, Torsten Sattler, Mircea Cimpoi, Marc Pollefeys, Josef Sivic, Tomas Pajdla, Akihiko Torii. InLoc: Indoor Visual Localization with Dense Matching and View Synthesis. In: IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. [bibtex]
Our InLoc dataset contains RGB query images taken with an iPhone7 depicting indoor environments from the WUSTL RGBD dataset [1], taken after the original dataset was captured, and 6DoF reference poses which are manually verified to be used for evaluating visual localization methods. We also provide RGB perspective images and depth maps which are generated from RGBD scans originally provided by [1] and used as the database for the InLoc dataset in our paper.
Dataset construction tool : A GitHub repository that contains the tools for constructing the whole of InLoc dataset. Each component can also be downloaded from here:
InLoc demo : A Github repository that includes the Matlab scripts demonstrating our indoor visual localization (InLoc) on our InLoc dataset
Online evaluation tool
: We open an online evaluation tool for visual localization on the InLoc dataset. The tool accepts the localization results in text format. Please use functions/utils/ImgList2text.m in the GitHub repository above to convert result file to the proper text format.
[1] Erik Wijmans, Yasutaka Furukawa. Exploiting 2D Floorplan for Building-scale Panorama RGBD Alignment. In: CVPR 2017. Project page
This work was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers 15H05313, 17H00744, 17J05908, EU-H2020 project LADIO No. 731970, European Regional Development Fund under the project IMPACT No~.CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/15003/0000468.
Please send bug reports and suggestions to Hajime Taira (htaira[at]ok.ctrl.titech.ac.jp)